In this guide, you will learn how Google RankBrain works, how it affects the future of SEO, and how to do proper keyword research after the RankBrain update.
Let’s get going…
Introduction to RankBrain
Google’s end goal is to get searchers the information they’re looking for because when they do, those searchers will keep coming back. A few years ago, Google released its first artificial machine learning intelligence tool naming it RankBrain.
RankBrain enables Google to deliver results based on more than just keywords on the page. Now, it can connect similar search queries based on user intent and deliver relevant results, even if they don’t contain the exact keywords the user used to search for the content.

With this artificial intelligence tool, Google has changed some of the SEO landscape. Your strategies need to change with it, so here’s a look at everything you need to know about Google’s RankBrain algorithm.
How does RankBrain work?
RankBrain’s goal is to help Google better understand search queries and the searcher’s intent. Using this tool, Google can learn more about content on a webpage without looking at just keywords.
Below are the main tasks the algorithm looks at.
1. Plural Queries
Before RankBrain keywords and phrases used to have to be exact to rank well.
For example, if you searched for a smartphone, web pages with information about smartphones (plural) wouldn’t show up.
By making the word plural, Google (in most cases) used to recognize this as a different phrase.
But now that has been changed as you can see in the screenshot below…

2. Synonym Queries
Before RankBrain, Google had no way of knowing that a webpage was using a synonym for a search query but still delivered information that helped the reader.
Let’s look at some examples of search queries that Google now can see are really just different ways of searching for the same thing:
- Best nail salons near me
- What are the best nail salons in my city?
- Top 10 nail salon places in my area
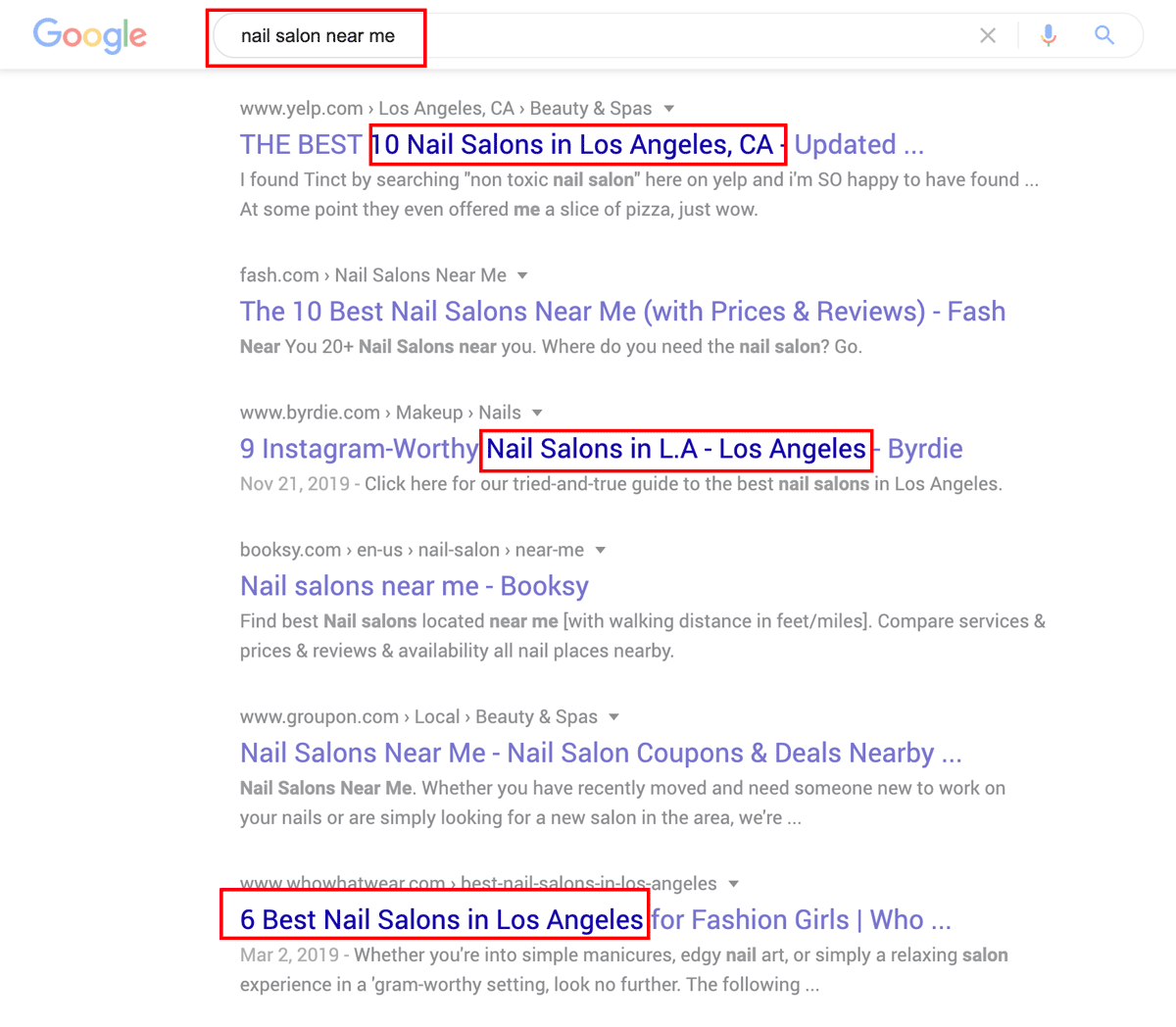
In all these queries, the searcher’s intent is to find a local nail salon.
Let’s look at a few other related quarry examples!
Before implementing RankBrain, a search for “European sports cars” would give you varied content because you would be getting results for “European” “sports” and “cars”.
This means that you would not only see results in vehicles from Europe but also soccer or rugby, which are popular sports from the region.
But now Google is smart enough to know that Lamborghini, Ferrari, and Porsche are all European sports cars.

One more example, if you were to search for “Russian television network” you will now get hits for RT or STS, even if they don’t have the words “Russian television network” in their content.
Google understands that those television networks are Russian and that they are popular and relevant to the search.

With RankBrain, Google can better understand these types of queries and deliver results for the overall topic instead of just the keywords.
How Does RankBrain Affect SEO?
Although RankBrain is changing the SEO strategy of keyword optimization by learning more about a user’s intent, that does not mean SEO strategies are dead. Instead, it means that SEO strategies need to adapt.
Your old content that’s optimized for a keyword is not suddenly irrelevant so long as it’s answering the searcher’s query.
To be clear, RankBrain does not mean SEO is worthless or not worth investing in. It means that you have to start with great content and focus it around answering your customers’ questions instead of just optimizing content for a keyword.
To put all that in super simple terms, RankBrain affects SEO by reducing the importance of keyword matching and increasing the importance of your content delivering the information the searcher is seeking.
RankBrain makes the SEO process more simple and pairs query with content that is relevant to the search.
What is the Future of SEO?
Now that you know what RankBrain is and what it’s doing to SEO, how do you move forward with an effective strategy that wins?
Here’s a look at the future of SEO and keywords.
- Condense your articles focused on the same topic into one “pillar post” that goes in-depth on the topic. Instead of having an article targeted at “nail salon” and another on the plural form “nail salons,” go back and combine these articles into one.
- Local SEO is also adapting. If you own a local nail salon, you don’t need to put your city name after every time you say the words “nail salon.” Google is smart enough to know your location! Instead, we recommend you to follow these suggestions: How to Create Localized Content to Attract Local Buyers.
- Adapt your content’s format to match the user’s intent. For example, let’s say you have an article about salon tips. But really, people are looking for a top 10 list of the best nail salons near you. Consider changing the article to be a full listing instead of just giving tips about nail salons.Remember, RankBrain gets to the user’s intent, so you need to deliver content that fulfills their queries, not just their keywords.
Ultimately, you need to stay focused on delivering consistent, valuable content.
Google may use your past successes in satisfying user intent to rank content for future related queries. Changing up your content’s format or delivery constantly might produce lower results than consistent, quality results.
The main takeaway here is that the future of SEO means being flexible and adaptive. You have to keep up to date on trends and search queries for your industry to continuously adapt your content to meet the needs of the user’s search query intent.
Keyword Research After RankBrain
Keyword research is not dead in the RankBrain era of Google. You’ll still need to create effective and relevant content based on what people are searching for. Now, Google will add context as a layer of complexity for ranking your content.
Do not stop doing keyword research before writing content. Instead, adapt your keyword research to focus more on user intent and how they search for information related to your topic.
Today’s keyword research requires that you go through a few steps.
- Gather all keywords relevant to your audience.
- Make keyword groups based on similarities.
- Evaluate user intent for a group of keywords.
- Research content that will serve the user’s intent for that keyword group.
Let’s look at an example of a search query for car rentals. You might have a list of keywords that looks like this:
- Car rental cost
- Compact car rental cost
- Average car rental cost
- Cost to rent a car
- Rental car costs
- Luxury car rental
- Cost for a luxury car rental
- Luxury car rental models
- Full-size car rental
- Car rental for a full-size car
That’s 10 keywords associated with the topic of car rentals. Before, you’d take each one of these keywords and write an article optimized for that one keyword. In the RankBrain era, you’ll now write one high-quality article that answers the searcher’s query.
Group these keywords under categories. From the listing above, a few recurring themes are: cost and luxury car rentals. So we know people are especially concerned with how much renting a car costs and what kinds of cars you can rent in the luxury category.
Now do a query for each of these subtopics and see if Google returns different results or if the overall theme of a car rental trumps these topic subsets of cost and luxury.
This will give you an idea of whether or not you should use all 10 keywords as one group for one webpage or if you should separate the keywords into separate pages or articles.
How to Do Keyword Research After the RankBrain Update
With your keyword groups created, you can now learn more about the specific questions people are asking related to your keywords.
Answer the Public is a great free service that allows you to input a keyword to see questions and queries people ask related to that keyword.
Using this tool, you can learn more about the searcher’s intent behind looking up information for their car rental.
To use the tool click on the link above. There is a search option on the home page, type your keyword hit enter.
Once the tool brings up the results, click on Data.

These specific questions can help you learn more about what the user is hoping to learn from their searches outside of the basic keywords.
The final step in your keyword research is to decide what type of content meets the user’s query intent the best. Your content types might be different for each keyword group, even though the overarching topic is car rental.
For example, the article for the cost-related group might be a breakdown of the average budget necessary for a week-long rental or a monthly rental. The article for the section on luxury car rentals might be “Cost-efficient luxury car rentals you’ll love driving.”
The best SEO strategy moving forward is to think about how a user might seek content related to your topic. Write your content as if you were having a customer service conversation with your target audience. Explain the topic in simple and easy-to-understand terms and deliver the answers they’re seeking.


